Risk Management
Risk management is the process of identifying, prioritising, managing and monitoring risks to information systems. Ensuring architectures and systems remain secure in today’s complex and ever-changing environment is an integral part of any cyber security strategy.
What is the risk management process?
In order to successfully manage risk you need to understand the risk environment you operate in. This means defining the appetite for risk. The route to this is to assess and identify risks posed to your enterprise. Once you’re aware of these risks you need to record and triage identified risks.
Identify controls to:
Continual management
It is crucial to monitor control effectiveness and continually risk manage and assure all enterprise security activities.
Everyone in the organisation plays a role in risk management. It’s important that all employees understand security best practices and execute these appropriately in their individual roles. Effectively managing cyber security risk means all departments of an organisation must operate with clearly defined roles and be tasked with specific responsibilities.
Before an organisation can identify cyber security risks they need to understand their objectives.
With this understanding they can then define a risk appetite, this is the amount of risk that you can tolerate in pursuit of its objectives.
With the understanding of its objectives and it’s risk appetite you can then identify risks.
This is achieved by undertaking a risk assessment.
A risk assessment is essentially the assessment of the risk posed to an organisation.
With a defined appetite risk will be assessed.
There are multiple approaches and standards for risk assessment but the following needs to be discovered:
- Threat sources
- Threat events
- Vulnerabilities.
For a risk assessment to be effective it needs to defined as the likelihood that a threat source will trigger a threat event which will in turn exploit a vulnerability and the impact of this occurrence.
Put simply risk is likelihood and subsequent impact.
Threats and vulnerabilities differ with each organisation and capability.
Threats are discovered by undertaking threat assessments and conducting threat modelling.
Vulnerabilities are discovered by published libraries containing known vulnerabilities, like the NIST National Vulnerability Database (NVD).
Organisations can mitigate cyber security risks by understanding it’s objectives, defining a risk appetite and then conducting a risk assessment.
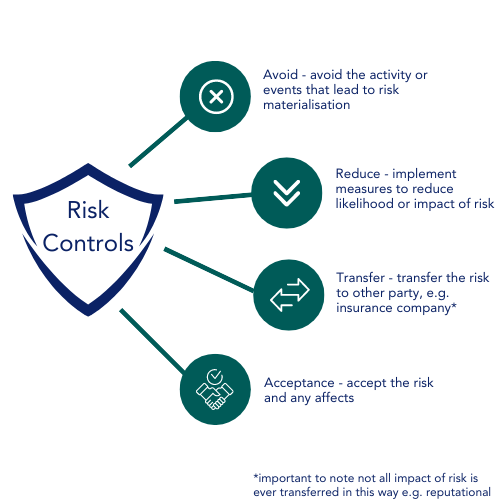
These identified risks are then triaged. Controls are then applied to mitigate these threats, these come in the form of:
- Avoid.
- Reduce.
- Transfer
- Accept
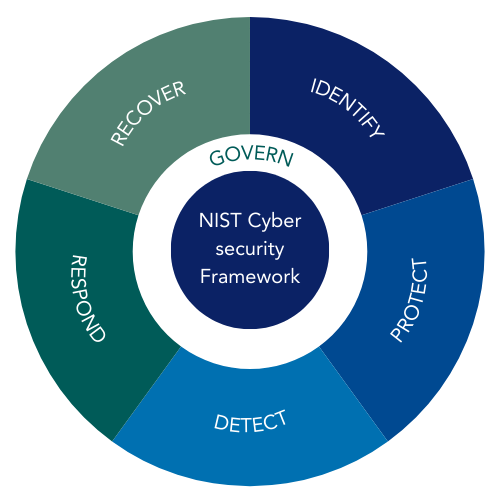
There are many frameworks used for risk management.
The most common are:
- NIST Special Publication 800-37: Risk Management Framework for Information Systems and organisations.
- NIST Cyber Security Framework (CSF).
- ISO 27001: Information security, cybersecurity and privacy protection – Information security management systems – Requirements.
